Researchers on the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have succeeded in elucidating the construction of particular photoreceptors. With their assist, it might be potential to change mobile actions on and off utilizing mild. This functionality may grow to be an vital software in organic analysis and medical purposes.
Researchers in biology and medication have lengthy dreamed of controlling the actions of cells with out, for instance, having to make use of chemical substances. In spite of everything, in a construction as advanced as a whole organism, undesirable side-effects can typically come up. The best answer would due to this fact be a sort of distant management for cells, which might enable the capabilities of particular person organs to be higher examined and understood, and will even be used for therapeutic functions. Distant management utilizing mild could be very best for this, as it might allow organs and tissues deep contained in the physique to be influenced in a really selective and non-invasive means. Nonetheless, such a course of additionally requires a mobile mild receiver within the related organs. The receptors that obtain mild impulses within the retina of our eyes – known as rhodopsins – could possibly be appropriate for this. With such photoreceptors, it is perhaps potential to change sure cell capabilities on and off utilizing a lightweight impulse. This might work extra quickly and in a extra focused method than medicine, which take a very long time to take impact and infrequently have undesirable side-effects as a result of they can not merely be activated in only one particular organ.
Within the neurosciences, one thing related is already working and is presently being examined in animal fashions to analyze mind illnesses corresponding to Parkinson’s and epilepsy: Mild-controlled ion channels from single-celled organisms are being included into neurons utilizing genetic engineering. Within the animal mannequin, these ion channels within the cell membrane open when uncovered to blue mild, for instance, and permit positively charged ions to circulate into the neuron. In a sequence response, additional channels open, creating {an electrical} sign – the neuron turns into lively.
A brand new sort of optogenetics
However such light-controlled ion channels solely work in nerve cells. The objective of this analysis, nonetheless, is to stimulate different cells and organs within the organism to manage quite a lot of bodily capabilities. For instance, one may examine the guts’s pure pacemaker, or the mechanisms of continual ache, anxiousness, despair, and different psychological diseases. It is perhaps potential to develop efficient cell therapies for hormonal malfunctions in addition to immune, coronary heart, and different illnesses, together with most cancers.
To this finish, researchers led by Gebhard Schertler of the PSI Middle for Life Sciences are engaged on a brand new sort of optogenetics. On this method, it’s mild receptors much like the rhodopsins in our retina that grow to be lively: Triggered by a lightweight pulse, they couple to proteins within the cell and thus provoke particular mobile signalling processes that happen in all organs. The PSI researchers have joined forces with main colleagues in Germany and England; collectively they have been awarded a coveted ERC grant: funding of almost eight million euros from the European Analysis Council. Their mission, Switchable rhodOpsins in Life Sciences (SOL), has three targets: 1. Discover rhodopsins that may do that and elucidate their construction to higher perceive how they work. 2. Modify such rhodpsins, utilizing molecular organic strategies, to optimise them for switching processes in numerous bodily capabilities. 3. Use the switches to higher perceive the signalling mechanisms of the proteins; use them as a software in analysis and, on that foundation, develop gene therapeutics.
The structural elucidation of proteins is a core competence of PSI, because of its high-resolution giant analysis amenities. And PSI researchers have now made two vital steps in direction of SOL’s first objective, as they report in two new research: First, they succeeded find an acceptable rhodopsin and modifying it in such a means that it stays secure within the lively state and thus will be examined. And second, the construction of this lively state was clarified utilizing a cryo-electron microscope at ETH Zurich.
A change that bends and stretches
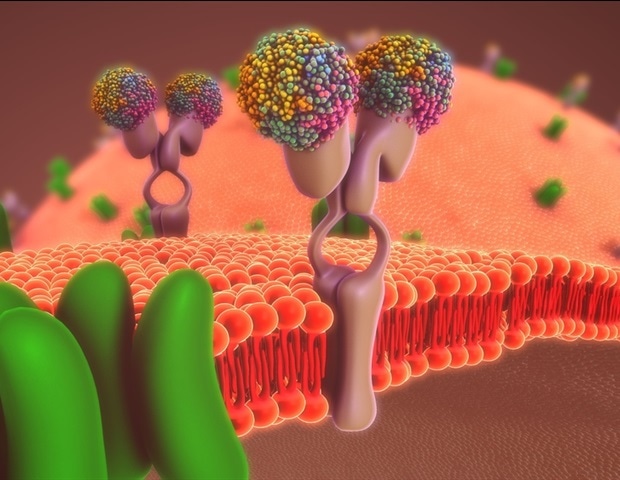
Rhodopsins are proteins. They’re among the many most vital photoreceptors within the animal world. They’ve an elongated molecule within the center, known as retinal, that’s derived from vitamin A. When a lightweight pulse hits this molecule, it absorbs the power and modifications its form inside a quadrillionth of a second. A curved molecule – known as the 11-cis type – turns into an elongated one – known as the all-trans type. By this transformation, the retinal additionally modifications the construction of the whole rhodopsin in order that it now can bind to different proteins within the cell membrane, so-called G proteins. Due to this fact, these light-sensitive rhodopsins additionally belong to the GPCR (G protein-coupled receptor) household, as rhodopsin-G protein complexes stimulate different proteins to react, triggering an entire collection of biochemical processes main, for instance, to the transmission of a visible sign to the mind.
The human physique possesses lots of of several types of GPCRs, that are positioned within the cell membranes, obtain alerts from the skin, and cross them alongside to the within of the cell. On this means, they management many bodily capabilities. That is why roughly 40 p.c of all medicines goal GPCRs with lively elements that dock onto their receptors.
The benefit of easy photoreceptors
Rhodopsins are discovered within the retina of the human eye. Within the rod cells, for instance, they’re liable for distinguishing between mild and darkish at night time. Nonetheless, like these of most vertebrates, these rhodopsins are monostable. Because of this as soon as the retinal has modified by mild, it leaves the protein and must be regenerated. Solely then is it obtainable for the following switching course of. That is too sophisticated to permit this molecule for use successfully as an optogenetic change, since enzymes would even have for use to regenerate it.
Many invertebrates, corresponding to squid, bugs, and spiders, have bistable rhodopsins. «From an evolutionary perspective, these are literally a extra primordial type of rhodopsins, and fewer delicate,» says Gebhard Schertler. They provide benefits for optogenetics, nonetheless: The retinal stays within the protein after being switched on, and with a second mild pulse it will possibly instantly return to its authentic type and change the mobile course of off once more.
The rhodopsin of a leaping spider species, for instance, proved to be sturdy and straightforward to supply, not like different bistable rhodopsins. This certified it as a potential optogenetic change.
With the Swiss Mild Supply SLS at PSI, it was potential to find out the molecular construction of this spider rhodopsin in its inactive floor state. However earlier than it could possibly be used as an optogenetic change, its construction within the lively type additionally needed to be recognized exactly. This state, nonetheless, when the retinal is stretched and the rhodopsin binds to the G protein, is extraordinarily short-lived.
How one can make proteins glad
In a single examine, which lately appeared within the journal PNAS, lead creator Matthew Rodrigues now studies how they managed to stabilise the lively state to have the ability to elucidate its construction: by making a tiny modification to the retinal. «The properties of the retinal stay the identical, however the modification – one small extra molecular ring – ensures that it apparently suits higher into the binding pocket of the protein,» studies Rodrigues. «It stays there for hours. As we structural biologists say, it is glad.» Now the situations have been in place to look at the construction of the lively rhodopsin at the side of a G protein.
A blended protein
In a second examine, now printed in Nature Communications, first creator Oliver Tejero and final creator Ching-Ju Tsai did precisely that. «Nonetheless, as anticipated, it was discovered {that a} spider protein (rhodopsin) naturally by no means suits optimally with a human protein (the G protein),» says Tsai. «So we in contrast spider G proteins with these of people and assembled a chimera from each kinds.» The researchers changed the tip a part of the gene sequence of the human protein, which accommodates the code for the docking web site, with that of the spider.
With extra genetic modifications within the precise mild receptor, they addressed one other drawback: The spider rhodopsins are each activated and deactivated by mild of the identical wavelength. «Because of this a lightweight pulse produces a hopeless hodgepodge of activated and deactivated states in a cell pattern,» says Tsai. Naturally, that is unhealthy for a change that’s supposed to activate or off in a focused method. «With our modifications, we’ve ensured that switching on and off now takes place with totally different colors of sunshine.»
Nonetheless, such «color tuning» via genetic engineering is just simply starting. The subsequent step within the basic analysis into these new optogenetic switches will now be to learn the way the proteins concerned should be designed to allow management utilizing different colors of sunshine. This might then make it potential to selectively change totally different cell capabilities on or off. It is usually a matter of setting up the switches in order that they aren’t solely delicate to blue, orange, and inexperienced mild, but in addition, for instance, to infrared mild. «The massive query stays, if optogenetics is definitely for use in on a regular basis medical observe, how the sunshine will get to the rhodopsin,» says Matthew Rodrigues. «You possibly can implant the sunshine supply into the physique. However the way more elegant and gentler methodology could be to work with infrared mild. This will penetrate physique tissue.»
The most important a part of the protein engineering, mission chief Gebhard Schertler confirms, remains to be to return, now that the structural fundamentals are recognized. In the end, the objective is to place collectively an entire meeting package of light-activated GPCRs that can be utilized for numerous functions within the organism.
Supply:
Journal references:
- Tejero, O., et al. (2024). Energetic state buildings of a bistable visible opsin sure to G proteins. Nature Communications. doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-53208-2.
- Rodrigues, M. J., et al. (2024). Activating an invertebrate bistable opsin with the all-trans 6.11 retinal analog. Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences. doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2406814121.

