Researchers reveal how intestine microbes form metabolic methods to gasoline bigger brains, providing a glimpse into the evolutionary biology of primates.
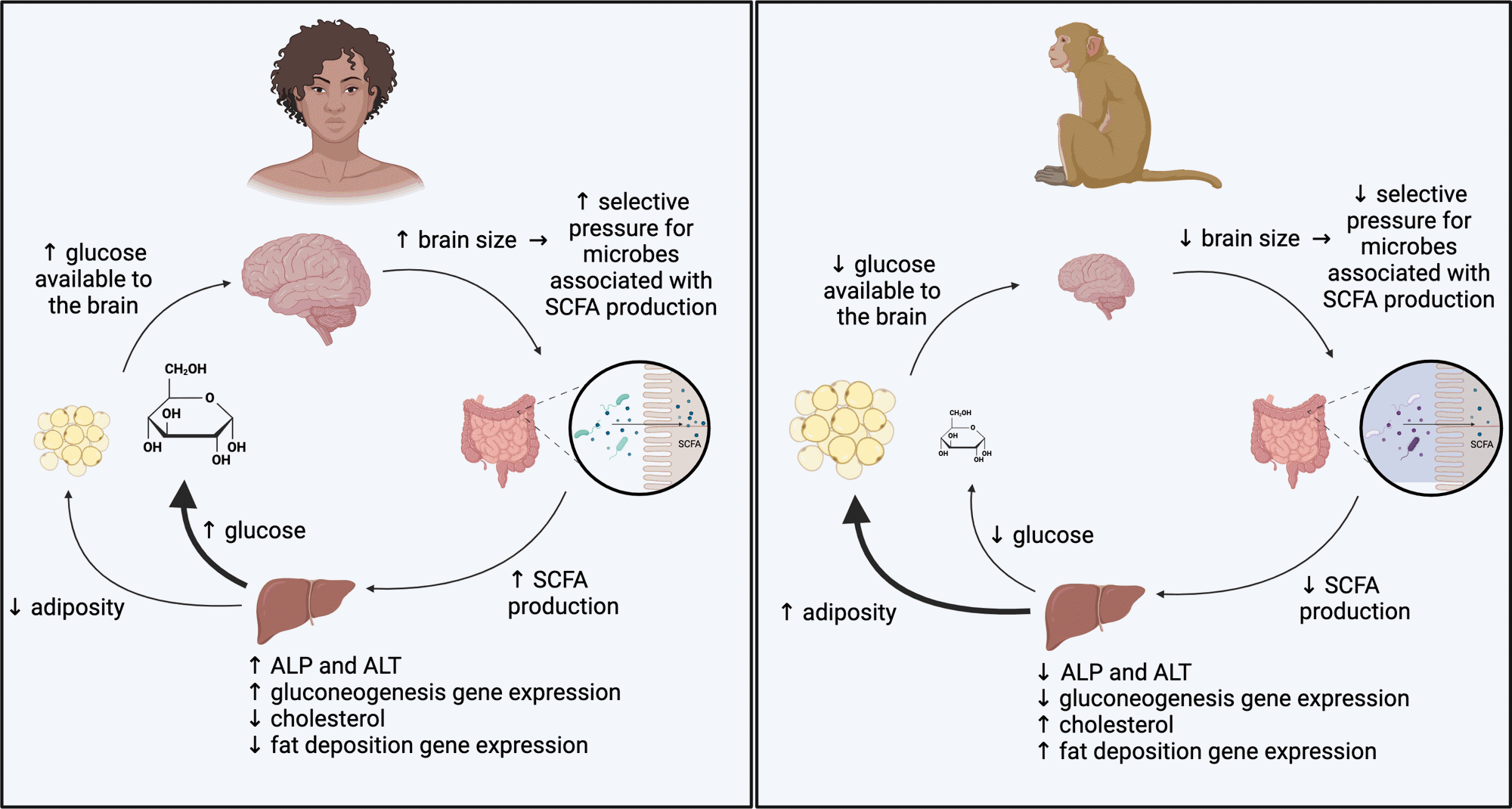 Putative mannequin for microbial influences on the metabolism of high-EQ and low-EQ primates. Our findings point out microbially mediated pathways by way of which the metabolism of high-EQ primates is biased in direction of vitality manufacturing and the metabolism of low-EQ primates is biased in direction of vitality storage.
Putative mannequin for microbial influences on the metabolism of high-EQ and low-EQ primates. Our findings point out microbially mediated pathways by way of which the metabolism of high-EQ primates is biased in direction of vitality manufacturing and the metabolism of low-EQ primates is biased in direction of vitality storage.
In a current research printed within the journal Microbial Genomics, researchers in the USA investigated the position of the intestine microbiome in influencing host metabolism throughout species, specializing in primates with various mind sizes. They transferred intestine microbiota from people, squirrel monkeys, and macaques to germ-free mice and examined how microbial communities contribute to metabolic traits that could be linked to mind vitality calls for and evolution.
Background
Massive brains are energetically expensive, particularly in primates, the place mind measurement usually correlates with elevated metabolic calls for. People, with the most important brain-to-body measurement amongst primates, present diversifications resembling increased glucose metabolism to maintain these energy-intensive organs. Nevertheless, the mechanisms driving such metabolic variations throughout species are poorly understood.
Present analysis has reported the involvement of genetic and epigenetic components in these metabolic variations, however their connection to systemic metabolism stays unclear. The intestine microbiome is an important regulator of host metabolism and produces metabolites resembling short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that affect vitality storage, glucose manufacturing, and fats metabolism. Moreover, whereas its position in metabolic illnesses, together with diabetes, is acknowledged, its contribution to interspecies metabolic variations, particularly associated to mind vitality calls for, is much less explored.
In regards to the Examine
Within the current research, the scientists hypothesized that variations within the intestine microbiota mediate metabolic methods and steadiness the vitality wants for mind perform in opposition to these for development and upkeep in primates with various mind sizes. The researchers carried out an experiment utilizing germ-free mice to analyze how the intestine microbiome influences metabolism in hosts with totally different mind sizes.
The intestine microbiota of three primate species, people, squirrel monkeys, and macaques, was transplanted into the germ-free mice to guage the consequences of microbial variations on host metabolism. People and squirrel monkeys have been chosen as “brain-prioritizing” species because of their bigger mind sizes relative to physique measurement, whereas macaques served as a comparability with a decrease brain-to-body measurement ratio.
Fecal samples from wholesome grownup primates, freed from antibiotics, have been collected, processed, and used to inoculate germ-free mice orally on a standardized food regimen for 60 days. Weekly assessments included weight measurements, meals consumption, and metabolic evaluations, with fecal and blood samples collected for microbiome and metabolite analyses. A glucose tolerance take a look at was administered to measure glucose regulation, and the mice underwent magnetic resonance imaging scans to evaluate physique fats distribution.
The researchers additionally used metagenomic and metabolomic analyses to determine particular microbial pathways and metabolites contributing to host metabolic traits. Excessive-resolution imaging and ribonucleic acid (RNA) sequencing of liver tissues supplied insights into organ-specific metabolic responses. The microbial composition within the mouse intestine was analyzed by way of 16S ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) sequencing, whereas metagenomic methods quantified SCFA manufacturing and microbial practical pathways.
Outcomes
The outcomes confirmed that the intestine microbiome considerably influences host metabolism in methods in keeping with the mind measurement of the primate species. Mice inoculated with intestine microbiota from high-brain-to-body measurement species, resembling people and squirrel monkeys, exhibited elevated vitality expenditure, increased fasting glucose ranges, and enhanced gluconeogenesis. Conversely, the mice inoculated with microbiota from macaques confirmed larger fats accumulation and weight achieve.
Moreover, the mice with microbiota from species with larger mind measurement consumed extra meals however displayed decrease physique fats percentages and slower weight achieve. Elevated ranges of SCFAs, resembling acetate and propionate, have been additionally noticed in these mice, suggesting a microbial contribution to elevated glucose manufacturing and lowered fats storage.
Metagenomic evaluation revealed that microbial pathways related to vitality manufacturing, resembling fucose and pyruvate metabolism, have been extra plentiful in high-brain-to-body measurement microbiota. Moreover, the expression of the genes related to liver perform in these mice revealed enrichment for pathways associated to vitality manufacturing, resembling lipid metabolism and gluconeogenesis. These modifications indicated metabolic programming geared toward prioritizing vitality for mind perform.
In distinction, mice inoculated with macaque microbiota exhibited microbial pathways favoring vitality storage. Their microbiome produced decrease SCFA concentrations and exhibited features aligned with fats deposition and decreased glucose manufacturing. These variations steered a trade-off between vitality allocation to the mind versus adipose tissues.
Curiously, human microbiota-inoculated mice confirmed distinctive metabolic profiles, with the best fasting glucose and propionate ranges, aligning with people’ distinctive mind vitality calls for. Regardless of consuming extra meals, these mice had minimal weight achieve, additional emphasizing the position of the intestine microbiota in metabolic regulation. Total, the outcomes highlighted the intestine microbiome’s potential to modulate host vitality allocation methods, reflecting the metabolic wants of the mind measurement of the host species and the related vitality calls for.
Conclusions
To conclude, the research demonstrated the very important position of the intestine microbiome in shaping host metabolic methods and supporting the vitality calls for of bigger brains in primates. The findings steered that microbial communities affect glucose manufacturing, fats storage, and vitality allocation, offering insights into evolutionary diversifications in mind measurement.
The researchers famous that their findings present a basis for exploring how microbiomes contribute to species-specific life historical past traits, resembling development, replica, and longevity. Future research might examine microbiome-host interactions throughout early developmental levels when mind vitality calls for peak.
Journal reference:
- Mallott, E. Okay., Kuthyar, S., Lee, W., Reiman, D., Jiang, H., Chitta, S., Alexandria, W. E., Layden, B. T., Sumagin, R., Manzanares, L. D., Yang, G.-Y., Luisa, M., Grey, S., Williams, L. E., Dai, Y., Curley, J. P., Haney, C. R., Liechty, E. R., Kuzawa, C. W., & Amato, Okay. R. (2024). The primate intestine microbiota contributes to interspecific variations in host metabolism. Microbial Genomics, 10, 12. DOI:10.1099/mgen.0.001322, https://www.microbiologyresearch.org/content material/journal/mgen/10.1099/mgen.0.001322

